In the quest for effective weight loss treatments, two GLP-1 peptides have gained considerable attention: Semaglutide and Tirzepatide. Both have demonstrated promising results in helping individuals lose weight, but they function slightly differently. If you’re exploring weight loss options and wondering which one is right for you, this guide will help compare the benefits, side effects, and how they work, allowing you to make an informed decision.
What are GLP-1 Peptides?
GLP-1 peptides, or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, are medications initially designed to treat type 2 diabetes by improving blood sugar control. However, studies have shown that these peptides can also lead to significant weight loss by reducing appetite, slowing digestion, and enhancing satiety.
Semaglutide: An Overview
Semaglutide is marketed under brand names like Ozempic® and Wegovy®. Initially approved for type 2 diabetes, it’s now widely used for weight management.
How Semaglutide Works
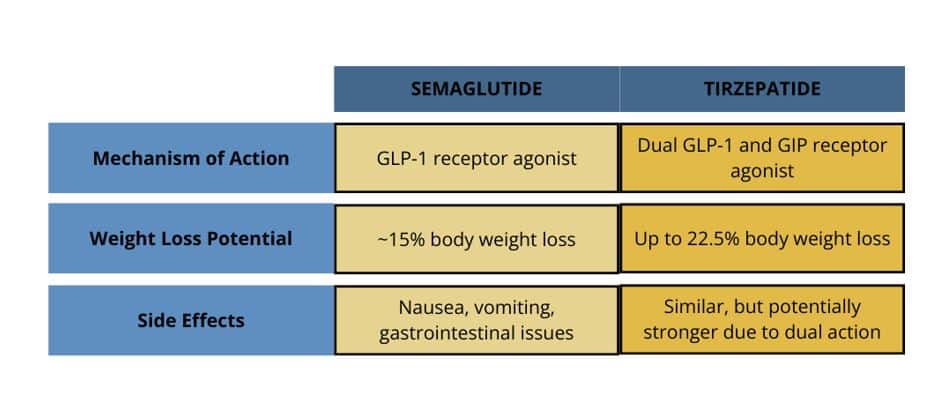
Semaglutide mimics the GLP-1 hormone, which triggers feelings of fullness after meals. It slows down the stomach’s emptying process, increasing satiety. It also directly acts on the brain to decrease the reward related eating behaviors and food cravings, helping individuals naturally reduce their calorie intake.
Benefits of Semaglutide
- Effective weight loss: Semaglutide has been shown to help individuals lose up to 15% of their body weight in clinical trials.
- Diabetes management: It’s highly effective in controlling blood sugar levels for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Once-weekly dosing: Semaglutide is injected once a week, making it convenient for long-term use.
Side Effects of Semaglutide
While effective, Semaglutide is associated with potential side effects:
- Nausea: This is the most common side effect, especially in the early weeks of treatment.
- Nausea while on semaglutide can sometimes be prevented and can generally be treated with added protein intake. Nausea can occur due to a slightly lower blood sugar level even when still in the normal range. The most common time people experience nausea while on semaglutide is the morning after the first injection or the morning after any dose increase. When most people wake up in the morning, their blood sugar is at its lowest point. The medication makes the blood sugar slightly lower than what it had been previously, potentially causing nausea. Increasing protein intake at the last meal before bed may help prevent the nauseated feeling. Treating nausea by eating a healthy protein source, stabilizes the blood sugar, teaching the body a new normal. If you treated the nausea by not eating, it may worsen if the blood sugar decreases. Eating carbohydrates or sugar when nauseated will increase the blood sugar, but the medication will cause it to drop faster than normal, which can also worsen the nausea. Healthy sources of protein should be utilized to stabilize the blood sugar and eliminate nausea while on semaglutide.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Some users experience vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Vomiting and diarrhea tend to occur after someone on semaglutide has eaten foods high in fats, sugars, or carbohydrates. Avoiding fried/greasy foods, sugary foods, and excess refined carbohydrates will help prevent these side effects.
- Constipation may occur due to the delayed gastric emptying and subsequently slowed digestion. Increased water intake, increased exercise, and increase natural fiber intake will help maintain regular bowel movements for most people. If supplemental fiber is taken, it is advisable to increase water intake further to avoid bulking stools.
- Hypoglycemia: Rarely, those with diabetes who take Semaglutide with other glucose-lowering medications might experience low blood sugar.
- Always discuss with your prescriber all medication that you currently take prior to starting a new medication. Those will diabetes on multiple medications, should be monitoring their blood sugar closely.
Tirzepatide: A New Contender
Tirzepatide, marketed under the brand name Mounjaro™, is a relatively new drug with dual-action. It acts on both GLP-1 and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) receptors, enhancing its effectiveness for both weight loss and diabetes management.
How Tirzepatide Works
Tirzepatide combines the benefits of GLP-1 and GIP, making it unique. GIP works alongside GLP-1 to reduce hunger and increase insulin sensitivity, contributing to greater weight loss results.
Benefits of Tirzepatide
- Superior weight loss: In clinical trials, Tirzepatide has demonstrated up to 22.5% weight loss, outperforming Semaglutide. Tirzepatide is the only medication that delivers weight loss results comparable to bariatric surgery.
- Dual-action: Its ability to act on two receptors provides enhanced blood sugar control and greater metabolic benefits. The response in the brain on the behavior and reward centers are more affected, drastically decreasing cravings. Tirzepatide is even being researched to help treat some addictions due to the changes in the brain reward center.
- Cardiovascular health: Tirzepatide may offer additional benefits for heart health, a key concern for those with obesity.
Side Effects of Tirzepatide
Similar to Semaglutide, Tirzepatide can cause:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common in the early stages of treatment.
- Injection site reactions: Some people report mild pain or irritation at the injection site.
- Potential for more pronounced side effects: Due to its dual-action mechanism, some users experience stronger side effects, although these often diminish with continued use.
- Tirzepatide is a stronger medication, starting at the lowest dose and increasing slowly are important to keep from having side effects. Following the recommended nutrition advice of increased water intake, increased protein, adequate fiber, avoiding fried/greasy foods, reducing refined carbohydrates, and reducing sugar are especially important to keep side effects at a minimum.
Semaglutide vs. Tirzepatide: Key Differences
While both peptides target weight loss, they differ in a few key ways:
Which GLP-1 Peptide is Best for Weight Loss?
If you’re primarily focused on maximizing weight loss, Tirzepatide may be the better option due to its superior results in clinical trials. However, if you’re looking for a more established treatment with a proven track record and slightly milder side effects, Semaglutide could be the better choice.
It’s important to consult your healthcare provider to determine which peptide is right for you based on your health profile, weight loss goals, and any other underlying conditions.
Conclusion
When comparing Semaglutide vs. Tirzepatide, both GLP-1 peptides are effective options for weight loss and diabetes management. Tirzepatide may offer greater weight loss potential, but Semaglutide has been used longer and may have fewer side effects for some. Ultimately, your choice should be guided by your individual needs and a discussion with your healthcare provider.
If you’re considering peptide therapy for weight loss, both of these GLP-1 peptides offer transformative benefits. Whether you opt for Semaglutide or Tirzepatide, taking that first step toward managing your weight and health is key.


